Welcome to Romo Healthcare Online store!
GET UP TO 8% DISCOUNT ON PRESCRIBED MEDICINE
Medicines

Supplements

Nutritional

Cardio Support

Sexual Welness

Women and Baby Care
Abdominal Pain

Homeo, Unani and Herbal
Medical Devices & Surgical
Anti-bacterial Infections
-debf2.png)
Diabetes Care

Beauty & Cosmetics

Stretch Mark Solution





Order with Prescription
Upload prescription and we will deliver your medicines
How does this work?


Watch Video


Prescription Upload




Women Health
View all
View all
20% OFF
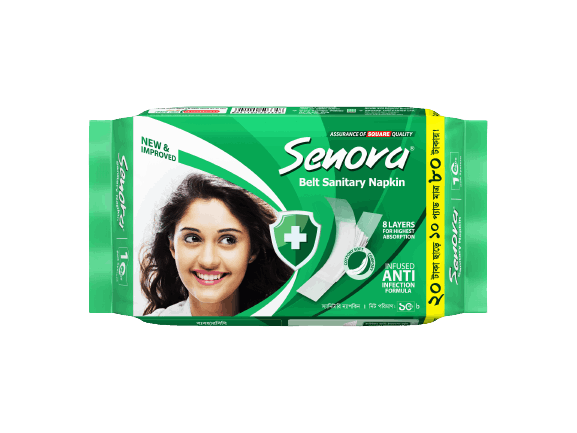

Napkin
২০ টাকা ছাড়ে ১০ প্যাড মাত্র ৮০ টাকা
Price: ৳80 ৳100
Health Concern
Stomach Care
Fever Care
Joint & Boan Care

Woman Health
Constipation
Cough and Flu
Diarrhea
Eczema
Gastric
Headache
Nasal
Vitamins
Devices
View all
View all
10% OFF
Machine
B-3 Basic Classic
Price: ৳3330 ৳3700

-(1)-6901f.png)

Our latest Health Blog
View All Blogs
If you take a look at any family, you can probably spot traits that family members share. Maybe they stand out as taller than just about anyone else at group events. Or you notice that a lot of them have free-hanging (or unattached) earlobes. Perhaps a family photo shows that just about everyone has dimples. There are also genetic traits that run in families that you can’t see. They can include risk factors for heart disease. Heart disease includes coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias and other heart problems, and it can affect people and families from all races and ethnic backgrounds. Maybe you have been struggling with very high cholesterol for a long time despite taking your medications, or maybe your mom or dad had a heart attack when they were young. When you know more about your risk, you can work with your health care provider to make smart decisions about your health. We connected with Esteban Astiazaran Symonds, MD, a medical geneticist with Banner – University Medicine, to find out more about the link between heart disease and family history. What are genetics? Genetics is the study of traits that are passed down through generations in your family. Your genes are part of your DNA, which is the code that makes you unique. Your genes determine things like your eye color and your height, and they also play a role in your overall health. Your genes can make you more or less likely to have certain health conditions, influence your metabolism and play a role in how your body responds to things like diet and exercise. While your genes are a factor in your health, they aren't the only thing that matters. Your lifestyle, environment, life experiences and more also make a difference. The role your genes play in heart disease Your genes can make you more or less likely to have risk factors for heart disease like high cholesterol, cardiomyopathies, atherosclerosis, irregular heart rhythms and other conditions. “Many different types of heart disease are influenced by our genes and can run in families,” Dr. Symonds said. “The most common heart diseases, like coronary artery disease and high cholesterol, are influenced by many different genes as well as environmental factors, such as diet, exercise and tobacco use.” Other types of heart disease can be caused by just one genetic change that has a strong effect. “These include rare conditions that mostly affect the heart's muscle (such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) or the heart rhythm (such as long QT syndrome),” Dr. Symonds said. Another example is a condition called familial hypercholesterolemia, which causes very high cholesterol levels and may lead to heart disease before age 50. If you know or suspect that you have certain heart problems or that they run in your family, talk to your health care provider. They can recommend the right screenings, lifestyle changes and treatments and take your family history into account when they are planning your care. Why it’s important to understand your family history Knowing the illnesses and conditions that your family members have can help you assess your own risk. This information can help you manage your risk factors and make lifestyle choices that may help keep your heart healthy. Be sure to share your family history with your provider. “Providing a complete family history gives your providers a better picture of your genetic risk. They will use this information in addition to your personal history, such as age, sex, race, cholesterol, blood pressure, etc., to determine your overall risk of heart disease,” Dr. Symonds said. In some cases, your provider may suggest genetic testing to evaluate your risk for heart disease. Genetic testing looks for specific genes that can run in families to see if you might be at higher risk for certain conditions. Your provider or cardiologist may recommend genetic testing if they suspect you have a heart problem that’s caused by a change to a single gene, or you have a relative who has a genetic disease. “Some clear indications for genetic testing include a personal or family history of sudden cardiac arrest, heart muscle disease, very elevated cholesterol, some types of arrhythmias and aneurysms, which are balloon-like bulges in the aorta or brain arteries,” Dr. Symonds said. If you’re concerned about your genetic risk factors, you can schedule an appointment with a genetic counseling clinic so you can better understand your risk and your possible need for genetic counseling. Many of these conditions occur as you age. “Providers will usually suspect a genetic cause when these symptoms occur at an earlier age than expected, when there is a significant family history or when other more common causes have been ruled out,” he said. By talking to a genetic counselor, you can better understand the emotions you might feel and decisions you might face if you have genetic testing. A counselor can explain the pros and cons of genetic testing and the effect the results might have on you and your family. Taking control of your heart health The goal of genetic testing is not just to identify risk, but to help you find ways to keep your heart as healthy as possible. Whatever your genetic risk is, the choices you make can shape the health of your heart. Keep the lines of communication open between you and your health care provider. Ask them any questions you have, so you can best understand your heart health and what you can do to improve it. Educate yourself about any heart conditions and risk factors. You and your health care provider can work together to create a heart health plan that takes into account your genetic risks and lifestyle choices. If you need to make changes, you can work together to set realistic goals. Be sure to see your health care provider for regular check-ups. That way, you’re more likely to spot any issues early, when they can be treated more easily. You can stay on top of any screening tests you need and make sure your lifestyle changes and treatment plan are working well. You can work together to make decisions about your treatments. And you’ll feel confident that you’re doing everything you can to keep your heart healthy. You may also want to connect with others in addition to your provider. Things like joining a fitness class, taking stress management classes or talking with friends and family can help you find the support you need. Joining a support group for people who have the same genetic risk factors may also be helpful. Sharing your experiences and talking to others on a path like yours can help you feel empowered and reassured. Lifestyle changes can reduce your risk Keep in mind that diet, exercise and stress management can help lower your risk of heart problems whether you have a family history of them or not. “Genetics is only one of several risk factors that influence the most common heart diseases. Eating a healthy diet, watching your weight, staying physically active, living tobacco-free and managing any other health conditions will have a huge positive impact in reducing your overall risk for the most common heart diseases,” Dr. Symonds said. A heart-healthy diet is important for everyone, and it can make a big difference for people who have a family history of high cholesterol. Getting regular exercise like walking, biking or aerobic workout classes can help counteract any negative genetics linked with heart health. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation or yoga can help counteract the effects of stress on the heart. The bottom line Your family history, or genetics, can influence your risk for some heart conditions and risk factors. By knowing your family history and sharing it with your health care provider, you can create a care plan that could include lifestyle changes, genetic testing, screenings or treatments. You and your provider or a Banner Health expert can work together to gather the information you need and make decisions about your care. Take our free Heart Age Test to learn more about your risk for heart disease.
Hypoglycemia – Every Diabetic Must Know!
The first step in managing diabetes is to know the signs and symptoms and be aware of the possible complications and educate yourself about managing them. Your doctor will guide you on various treatments, interventions and lifestyle modifications that are available. A person taking medications for diabetes must know about the risk of hypoglycemia or a sudden drop in blood sugar levels Understanding Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia is a medical term for low blood sugar levels. People with diabetes are more likely to experience hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Low blood sugar can also be caused by a few additional conditions. The supply of glucose to your brain must be continuous and consistent. Because it can’t store or produce its energy, your brain may be impacted if your glucose level decreases. When this happens, you could experience these hypoglycemia symptoms: Odd behaviour, confusion, irritability, dizziness Visual abnormalities, such as double or blurred vision (uncommon) Loss of consciousness (uncommon) Seizures (uncommon) Other physical symptoms of hypoglycemia include: Anxiety Palpitations Excessive hunger Sweating Shaking of hands and feet Headache As these symptoms aren’t exclusive to hypoglycemia, if you’re diabetic, you should check your blood sugar level whenever these symptoms appear. It’s the only method to figure out if they’re caused by a blood glucose issue or anything else. How to Manage Hypoglycemia? The first step towards the treatment of hypoglycemia is consulting a trusted doctor or diabetologist who will be able to advise a specific treatment suited to your case and symptoms. The recovery plan will most likely be divided into two parts – what action to take right away to restore normal blood sugar levels and what needs to be done in the long run to identify and treat the source of hypoglycemia. Your doctor will start the treatment for hypoglycemia by first determining the symptoms you’re having. Taking glucose tablets or eating sugar, such as sweets or fruit juice, may usually help manage early symptoms and return your blood sugar to a safe level. If your symptoms are more severe and you’re unable to consume sugar by mouth, you may require a glucagon injection or an IV glucose infusion by a healthcare professional. The 15 Rule to manage hypoglycemia If your blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, use the 15-15 rule to raise it: Eat 15 grams of carbs (3 – 4 tablets of glucose or a half cup of fruit juice or 1 tablespoon of sugar or honey) and check your blood sugar after 15 minutes. Have another serving if it’s still below your goal range (understand your goal range from your doctor). Repeat these procedures until you’ve reached your desired range. Eat a nutritious lunch or snack once it’s back in range to keep it from dropping too low. What is the long-term treatment for hypoglycemia? Your doctor will want to work with you to figure out what’s causing your low blood sugar. Counsel you about taking your medications and meals timely. They may advise you to revise your diet plan and may also alter your dosages if you’re currently taking medication or find a new way to manage your lifestyle.

Practical Tips for Adherence to Diabetes Management Journey
Being diagnosed with diabetes can be overwhelming, but it’s essential to remember that managing the condition is a journey, not a sprint. A crucial aspect of successful diabetes management is adherence to the treatment plan, diet and lifestyle changes prescribed by your healthcare team. By incorporating these recommendations into your daily routine, you can take control of your health and improve your overall well-being. 1. Understand Your Treatment Plan Knowledge is power when it comes to managing diabetes. Take the time to understand your treatment plan, which may include medications, insulin, or other therapies. Familiarise yourself with the proper dosages, timing, and potential side effects. If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your healthcare provider. A clear understanding of your treatment plan is the foundation for successful diabetes management. 2. Create a Routine Consistency is key in managing diabetes. Establish a daily routine that includes regular meal times, medication schedules, and consistent physical activity. A structured routine helps stabilise blood sugar levels and makes it easier to adhere to your treatment plan. Set reminders on your phone or use a medication organiser to ensure you never miss a dose. 3. Balanced Nutrition is the Key Eating a balanced and nutritious diet is vital for diabetes management. Focus on a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Monitor your carbohydrate intake, and choose complex carbohydrates over simple sugars. Portion control is crucial to avoid spikes in blood sugar levels. Consulting with a registered dietitian can provide personalised guidance on creating a diabetes-friendly meal plan. 4. Regular Physical Activity Exercise plays a crucial role in diabetes management by improving insulin sensitivity and aiding in weight management. Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week. Consult with your healthcare team before starting a new exercise regimen, and choose activities that you enjoy to make them a sustainable part of your routine. 5. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly Frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels provides valuable insights into how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for monitoring and record your results regularly. This information can help you and your healthcare team make informed decisions about adjustments to your treatment plan. 6. Stay Hydrated Proper hydration is essential for overall health, and it can also support diabetes management. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps regulate blood sugar levels and can prevent dehydration, a common concern for individuals with diabetes. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day, but individual needs may vary. 7. Build a Support System Living with diabetes can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Building a support system of friends, family, and fellow individuals with diabetes can provide encouragement, understanding, and motivation. Share your goals and challenges with your support network, and don’t hesitate to ask for help when needed. 8. Prioritize Stress Management Stress can impact blood sugar levels, making it essential for individuals with diabetes to prioritise stress management. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine. Finding healthy outlets for stress, such as hobbies or spending time in nature, can contribute to overall well-being. 9. Regular Check-ups with Healthcare Providers Scheduled check-ups with your healthcare team are crucial for monitoring your overall health and adjusting your treatment plan as needed. Be proactive in scheduling and attending regular appointments with your healthcare provider, endocrinologist, and other specialists involved in your diabetes care. Open communication with your healthcare team is vital for addressing any concerns or challenges you may face. 10. Celebrate Achievements, Learn from Setbacks Managing diabetes is a continuous learning process. Celebrate your successes, whether big or small and use setbacks as opportunities to learn and adjust your approach. It’s normal to face challenges along the way, but by staying committed to your treatment plan and making necessary adjustments, you can navigate the diabetes journey successfully. Adhering to a diabetes treatment plan and making lifestyle changes can be challenging, but it’s a crucial investment in your long-term health. By understanding your treatment plan, creating a routine, and embracing a balanced lifestyle, you can take control of your diabetes and live a fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone – your healthcare team and support network are there to guide you every step of the way. Disclaimer: The information included on this site is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of unique individual needs, the reader should consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for the reader’s situation.





-499a5.png)
-b89bf.png)







-e5550.png)

-33fe8.png)
-4f2de.png)
-c54e7.png)

-f2789.png)
-61032.png)




-bd122.png)
 banner
banner  Feb 12, 2024
Feb 12, 2024

